
XJExpress-FPGA
Ultra-Fast FPGA-Accelerated Flash Programmer
In stock
XJExpress-FPGA is an advanced flash programmer for maximum-speed in-system programming (ISP) via an FPGA, attaching via the JTAG port.
XJExpress-FPGA provides pre-configured programming solutions for the flash memory connected to FPGAs in your design, including FPGA-based SoCs such as Xilinx Zynq™ and Intel Cyclone® V. The functional capabilities of the FPGA are harnessed to provide the fastest possible programming speeds, without requiring you to do any FPGA development.
Whether you have a single flash memory or multiple devices to program, and whether you have devices connected in series to expand the address space, or in parallel to make a wider data bus, XJExpress-FPGA can speed up your programming operations.
Key benefits
Cut flash programming times
Programming speed often limited by flash device write speed. Intelligent erase functionality only performs erase operations when necessary.
Wide range of flash device types supported
SPI, QSPI, parallel NOR flash devices supported. Support for NAND devices available on request.
Streamlined workflow
Use single controller and single project to both program and test.
No FPGA development required
XJExpress-FPGA comes pre-configured to use a chosen FPGA or FPGA SoC model, along with the selected flash memory part.
Custom devices, configurations and operations
Different configurations of flash chips and programming files can be supported.
Powered by XJFlash
Delivers the programming capabilities of the XJTAG Test suite’s XJFlash Module, but in a standalone product.
Wide range of FPGAs/SoCs supported from major manufacturers
Performance
XJExpress-FPGA will automatically step through four stages each time a flash device is programmed:
Initialisation – The FPGA connected to the flash is configured with the XJExpress-FPGA image required for the target board.
Erase – The flash can be erased using one of two algorithms. The basic erase will simply erase all blocks within a defined range (this may be the whole flash or just the space needed for the image to be programmed). The more intelligent erase will use the fact that it is quicker to read the flash than to erase it; as such it reads from each address and only starts erasing if some data is found. This step can be skipped if it is known that the flash will always be blank before it is programmed.
Program – Data from the target images is streamed into the FPGA through its JTAG port. The FPGA then programs this data into the connected flash(s). Multiple files can be specified and programmed at defined offsets. This step can be bypassed if only verification is required.
Verify – The verification checks every byte in the flash against the specified file(s), ensuring there are no data bit errors. This step can be bypassed if only programming or erasing is required.
Effect of intelligent erase algorithm
Example timings for a Spartan-6 XC6SLX9 programming a 16 Mbit pseudorandom data file into the FPGA’s SPI configuration PROM with TCK at 10 MHz:
Effects of changing flash memory size
Example Timings Using a Xilinx Zynq™-7000 series SoC
A 256 Mbit file can be programmed into a SPI NOR flash and verified in around 46 s, depending on the TCK speed and the memory type being used*; 32 Mbit of code takes just over 7 s.
Adding an initial erase cycle adds only 3.1 s for an empty 256 Mbit flash, or 54 s for a full one. That drops to 0.4 s and between 6.5 and 9.2 s respectively for a 32 Mbit device.
* TCK = 66 MHz, pseudorandom data file. Time varies with flash type.
Example Timings Using a Xilinx Zynq™ UltraScale+™ series SoC
A 256 Mbit file can be programmed into a SPI NOR flash and verified in around 42 s, depending on the TCK speed and the memory type being used**; 32 Mbit of code takes 7 s.
Adding an initial erase cycle adds only 2 s for an empty 256 Mbit flash, or 57 s for a full one. That drops to 0.3 s and 6.9 s respectively for a 32 Mbit device.
** TCK = 30 MHz, pseudorandom data file. Time varies with flash type.
Requirements
In order to use XJExpress-FPGA, all of the data bus, address bus and control signals on the flash device must be controllable from an FPGA. In most cases, they will be controlled by an FPGA on the UUT. The FPGA must be accessible via its JTAG Test Access Port (XJExpress-FPGA needs access to the JTAG signals and any signals required to keep the FPGA in JTAG mode during the programming operation must be set by the user or made accessible). The flash device can be a configuration PROM for the FPGA, or a flash device connected to any general purpose I/O pin. Connections between FPGA and flash can be direct, indirect, dedicated or shared:
Direct connections – YES


The flash is directly connected to the FPGA.
Indirect connections – YES

- The flash is connected to the FPGA via a buffer
- Some of the address signals are shared with the data signals and connected via a latch.
- There is another configurable device, such as a CPLD between the flash and the FPGA.
Shared connections – YES
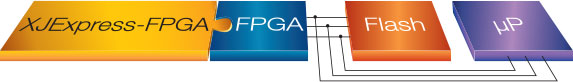
The flash is connected to the FPGA in one of the modes described above but these connections are shared with another device (such as a processor).
No connections – YES (with design changes)

If your design contains an FPGA but the flash is not connected in any of the configurations described, it may be possible to use spare pins on the FPGA to establish connections to the flash. These connections would not be used in the mission mode of the board but would allow you to use XJExpress-FPGA to perform fast flash programming. If your FPGA is already connected to the same address/data bus as the flash then this may not require many extra signals.
No FPGA – Not directly

Unfortunately, it is not possible to use XJExpress-FPGA if there is no FPGA. However, if it is possible to bring the connections of the flash to a header or test points on the board, XJExpress-FPGA can be used via those connections with an XJAccelerator card.
Alternatively, it may be possible to do fast flash programming using the debug interface on a processor – please contact us to see if you can use this approach on your board.
Compatibility
Supported FPGA families
- Altera (Intel) – Arria GX, Arria II GX, Arria II GZ, Arria V, Arria V GZ, Arria 10, Cyclone, Cyclone II, Cyclone III, Cyclone III LS, Cyclone IV E, Cyclone IV GX, Cyclone V, Stratix, Stratix GX, Stratix II, Stratix II GX, Stratix III, Stratix IV, Stratix V, Stratix 10
- AMD (Xilinx) – Artix-7, Artix UltraScale+, Kintex-7, Kintex UltraScale, Kintex UltraScale+, Spartan-3, Spartan-3A, Spartan-3E, Spartan-6, Spartan-7, Versal, Virtex-II, Virtex-II Pro, Virtex-4, Virtex-5, Virtex-6, Virtex-7, Virtex UltraScale, Virtex UltraScale+, Zynq-7000, Zynq UltraScale+
- Lattice – MachXO2, LatticeECP3, LatticeXP2
- Microchip (Microsemi) – IGLOO2, ProASIC3, ProASIC3E, ProASIC3L, SmartFusion2
This list is continuously growing, so contact us for the latest details.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Flash Programming Solutions
| XJExpress | XJExpress-FPGA | XJDeveloper & XJRunner | |||
| Native | XJFlash | XJDirect | |||
|
Performance |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI NOR Flash Indicative Speed | 12Mb/s | 12Mb/s | 10kb/s | 12Mb/s | 3Mb/s |
| Speed Limiting Factor* | Target Memory | Target Memory | Boundary Scan | Target Memory | Debug Interface** |
|
Connection |
|||||
| Controller Connection | USB | USB, PXI | USB, PXI, ATE | USB, PXI, ATE | USB, PXI, ATE |
| Programming Type | Direct | Indirect-FPGA | Indirect Boundary Scan, Direct | Indirect-FPGA, Direct*** | Direct, Indirect-Processor |
| Intermediate Devices | None | FPGA | None, JTAG device | FPGA, None | None, Processor |
| Board Access | N/A | JTAG | N/A | JTAG*** | JTAG, SWD |
| Flash Interface Bus | SPI† | SPI†, Parallel, eMMC | SPI†, Parallel, I2C, eMMC, JTAG | SPI†, Parallel, eMMC | Internal, External SPI†, Parallel, I2C, eMMC |
|
Supported Devices‡ |
|||||
| SPI NOR Flash | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Parallel NOR Flash | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| NAND Flash | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| eMMC | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| MRAM | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| FRAM | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| NVSRAM | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| PCM | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| EEPROM | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
|
Interface & Control |
|||||
| Hardware Controller Included | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Application GUI | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Command Line Interface | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Control by API | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Logs | ✗§ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Lockable Project Format | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Integrated Into XJTAG Testing Suite | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
|
Configuration |
|||||
| Erase/Program/Verify Configuration | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Customisable Configuration | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Register Configuration | ✗§ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Auxiliary Pin Control | ✗§ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Auxiliary Device Control | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Target Configurations Included With Purchase | All | 1 | All | All | 1 |
| Full Device Library Access | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
|
Support |
|||||
| 1 year product warranty | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 1 year support and maintenance from XJTAG engineers (can be extended) | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
* in normal use, other limiting factors may cause restrictions for specific device types and configurations
** Ethernet or other fast buses can be used via XJDirect for faster programming
*** or directly with an XJAccelerator accessory board
† single, dual, quad and octal supported
‡ not all memory types are listed, please contact us for specific enquiries
§ coming in Q2 2026, available as a free upgrade
